How Pregnancy Can Temporarily Change Your Hearing
During pregnancy, your body goes through many changes, some of which may
Disclaimer: 3% Processing Fee for All Credit and Debit Card Transactions


During pregnancy, your body goes through many changes, some of which may
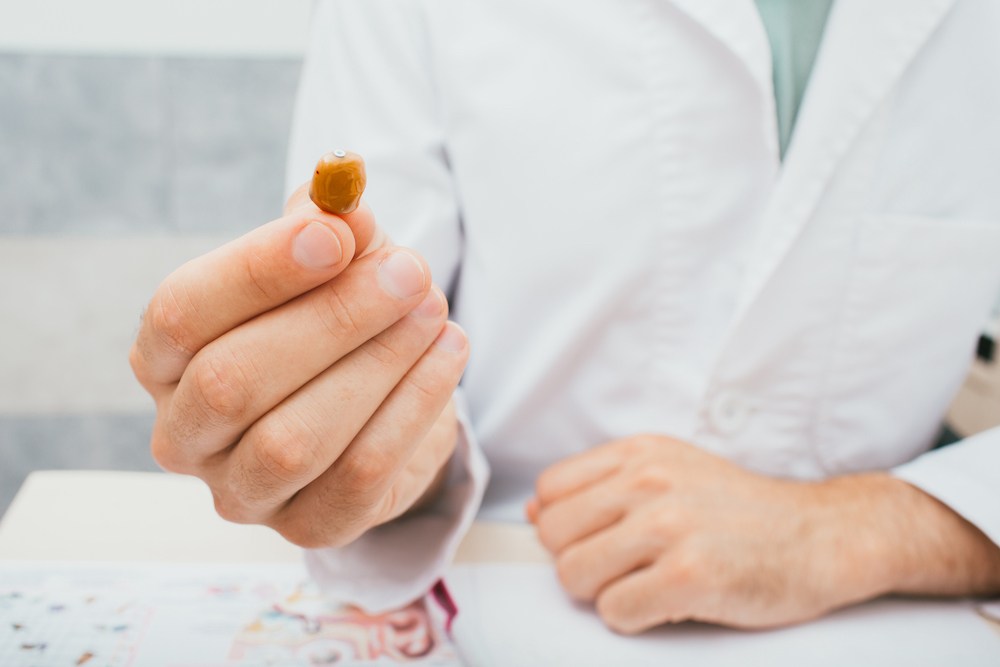
Keeping your hearing aids clean and well maintained is essential for
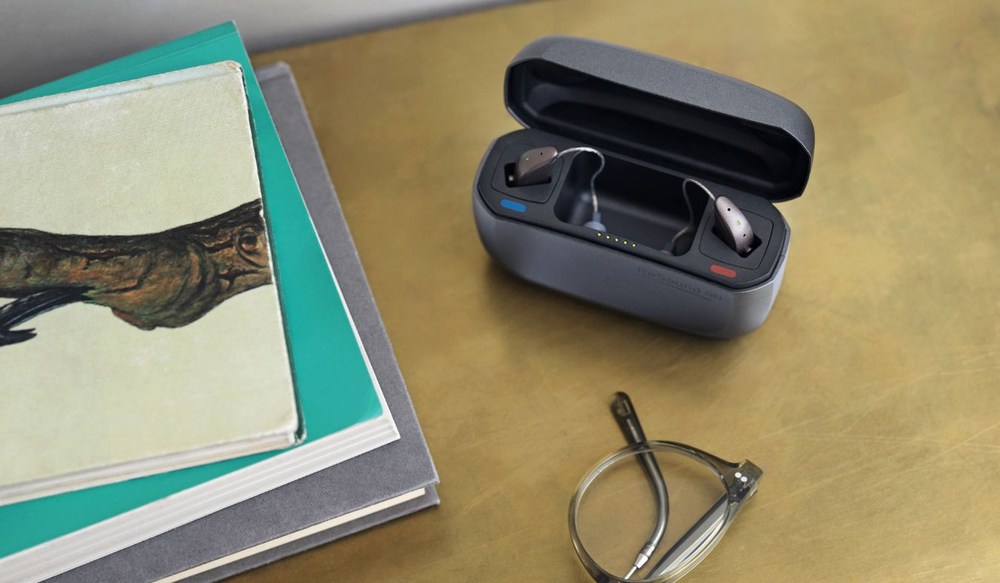

Choosing between rechargeable and battery powered hearing aids is an